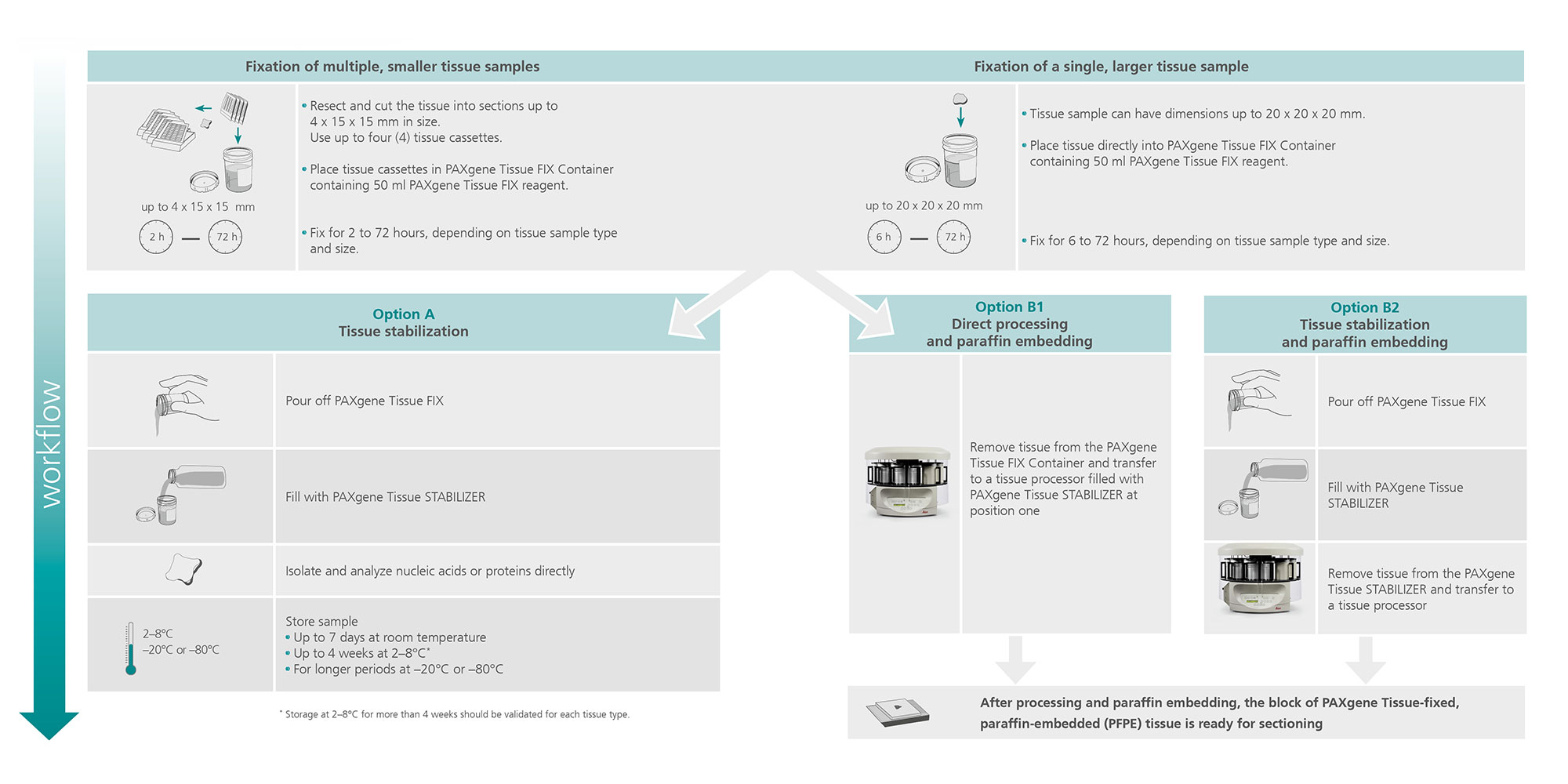
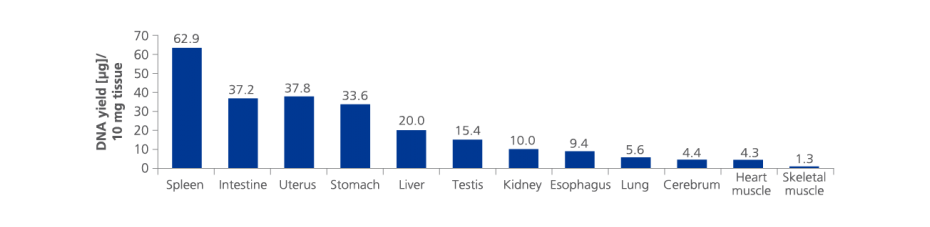
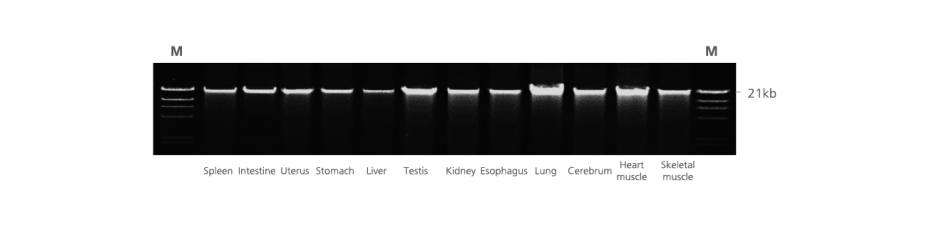
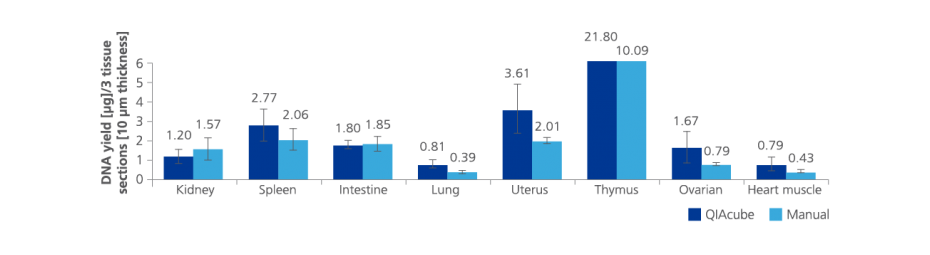
Performance
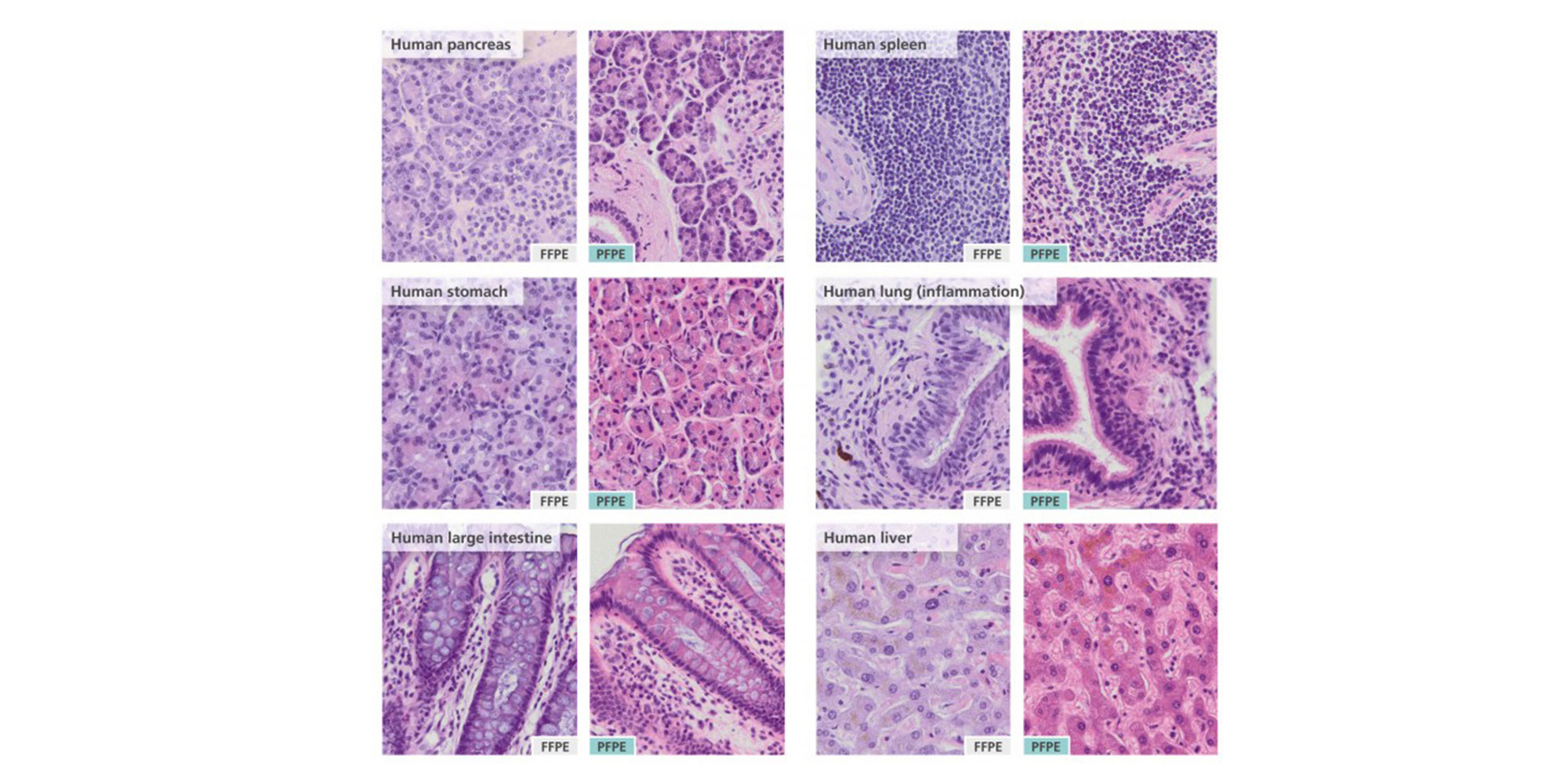
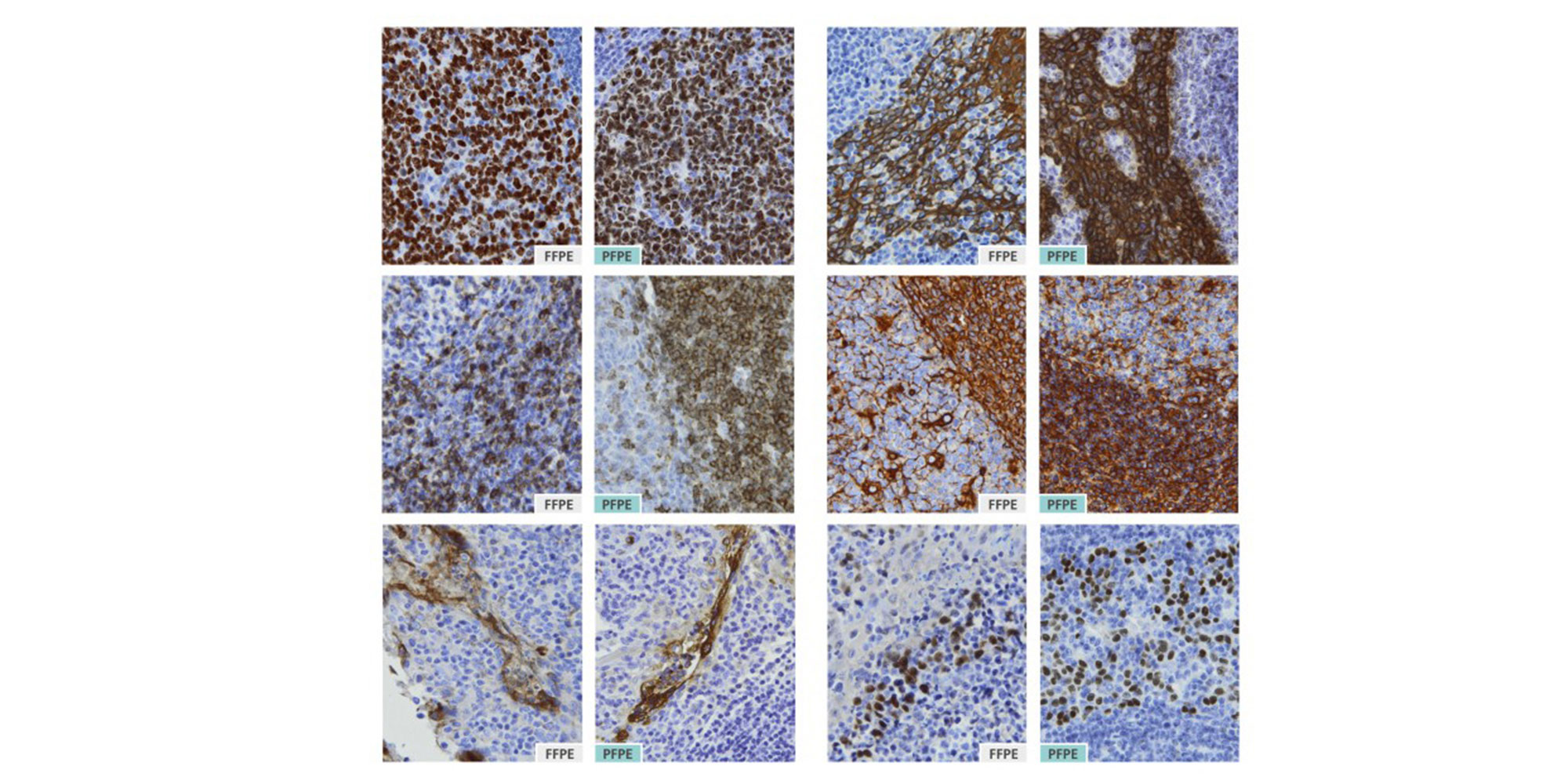
PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER Concentrate serves to stabilize and preserve tissue morphology and the integrity of biomolecules without destructive crosslinking and degradation found in formalin-fixed tissues (Figure 1 and Figure 2). While the stabilizing action of this agent is designed for tissues that have been previously fixed in PAXgene Tissue FIX, appropriately diluted PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER Concentrate can be used in paraffin-embedding with a tissue processor.
Enhanced storage
When tissues previously fixed in PAXgene Tissue FIX are stored in PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER, nucleic acids, proteins and morphology are stable for up to 7 days at room temperature (15–25°C) or 4 weeks at 2–8°C. Tissue samples can be stored in the PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER for longer periods at –20°C (–15°C to –30°C) or –80°C (–65°C to –90°C) without negative effects on the morphology of the tissue or the integrity of analytes.
Note: Specifications for storage conditions in PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER were determined using animal tissues. Storage at 2–8°C for more than 4 weeks must be validated for each tissue type.
Note: For storage at –20°C (–15°C to –30°C) or –80°C (–65°C to –90°C), use cryogenic vials with screw caps filled with PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER. For safety reasons, note that PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER contains 70% ethanol by volume.
High-quality biomolecule stabilization
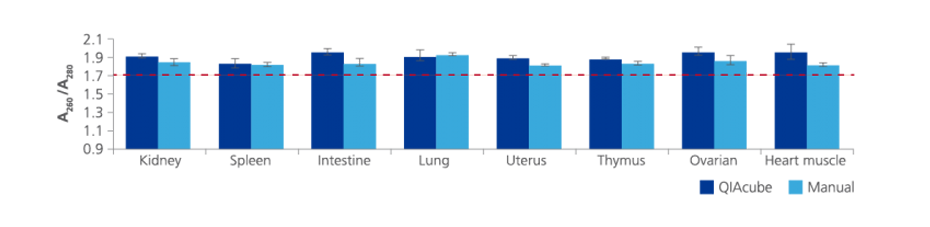
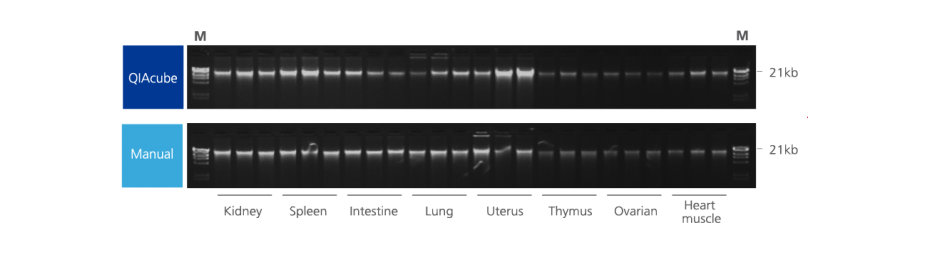
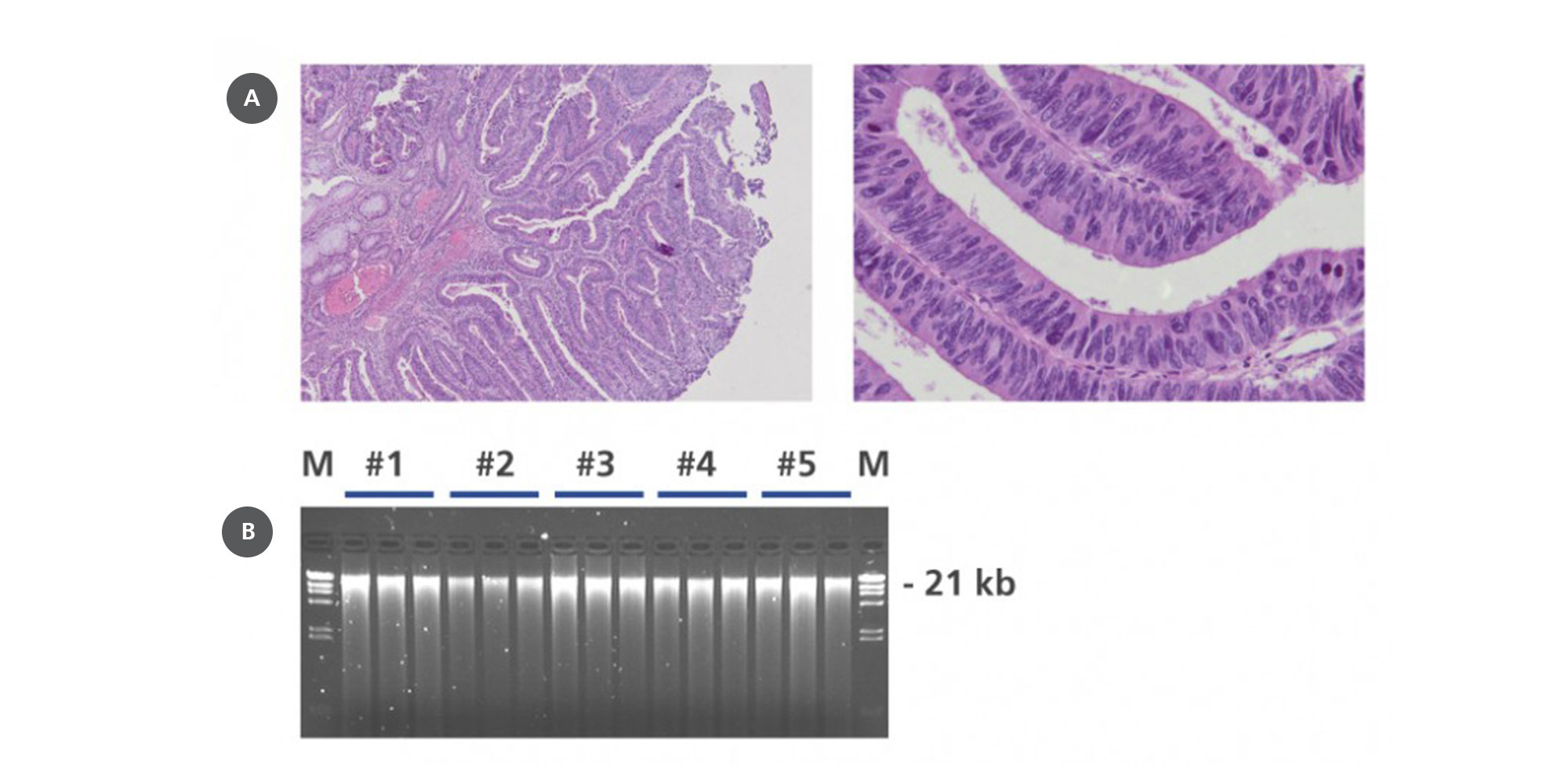
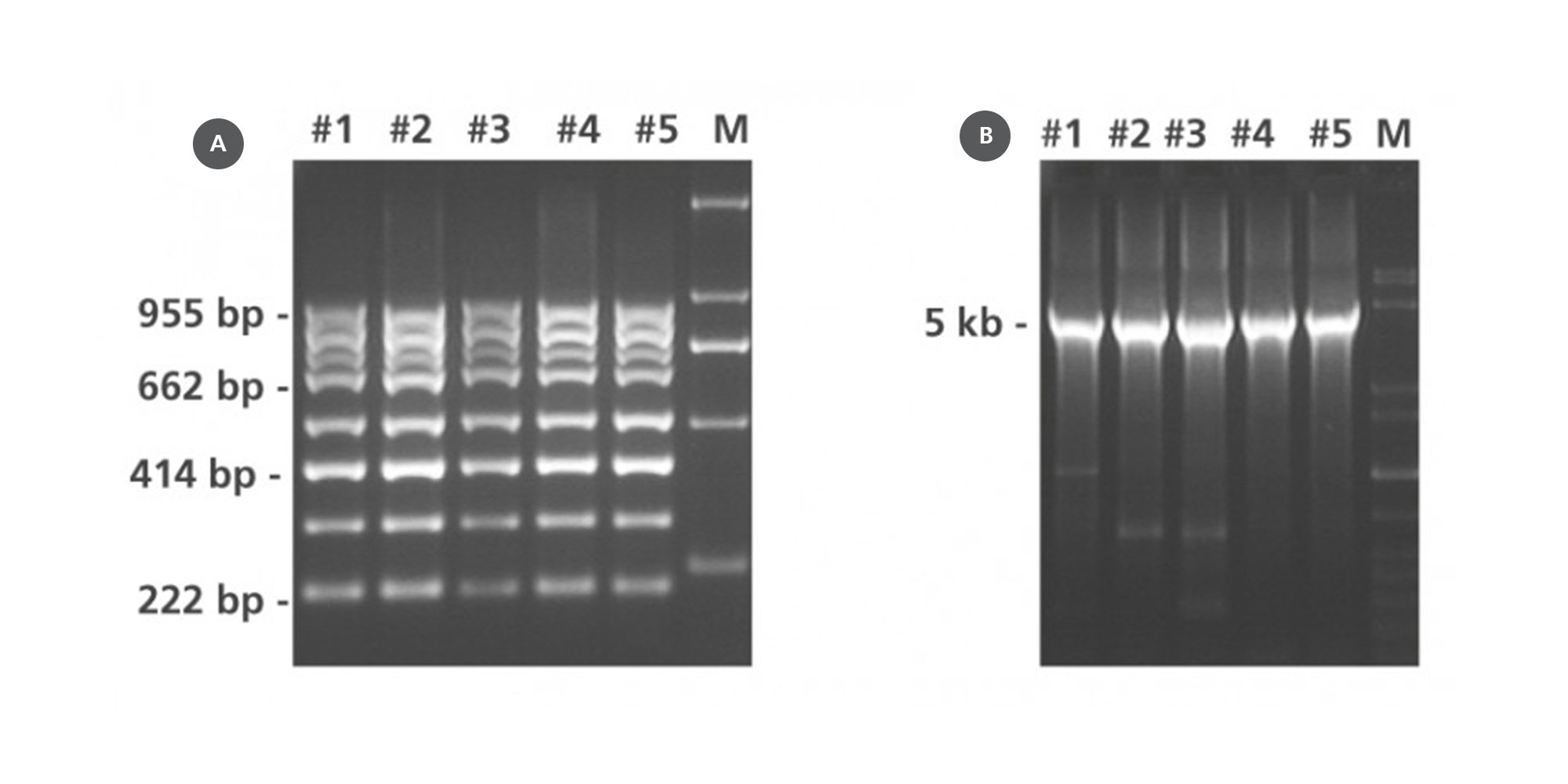
Nucleic acids and proteins of tissues stored in PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER or as PAXgene Tissue-fixed, paraffin embedded (PFPE) samples are stabilized and can be purified using the corresponding PAXgene Tissue Kit for RNA and miRNA or DNA. Use the Qproteome FFPE Tissue Kit for purification of proteins. Purified biomolecules are of high quality (Figure 3) and unmodified (Figure 4). The purified biomolecules are highly suited for a range of demanding downstream applications (Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7).
Principle
The formalin-free PAXgene fixation and stabilization products can be used as an alternative to traditional histology methods for tissue fixation and analysis because they enable comparable processing of tissue samples without the crosslinking and degradation observed in formalin-based systems. The PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER enables stabilization of tissue specimens previously fixed in a PAXgene Tissue FIX Container. The system facilitates preservation of tissue morphology and stabilization of biomolecules so that histological and molecular analyses, including RT-PCR, qPCR and next-generation sequencing, can be performed on the same tissue specimen.
Procedure
PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER Concentrate is diluted with ethanol to make PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER Reagent, which is designed to be used with tissues that have been fixed in PAXgene Tissue FIX. After fixation of tissue samples with the PAXgene Tissue FIX Containers for 2–72 hours, the fixative in the container is removed and replaced by PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER. Stabilized samples can be stored long-term in the STABILIZER or embedded in paraffin for histological studies. Nucleic acids and proteins can be isolated from the stabilized samples before or after embedding in paraffin. PAXgene Tissue STABILIZER Reagent can also be used in paraffin embedding with a tissue processor (Figure 9).
Applications
PAXgene Tissue-fixed (PF) and PAXgene Tissue-fixed, paraffin-embedded (PFPE) tissue samples can be used for (see References, Tissue Atlas):
- Histopathological staining, including hematoxylin & eosin (H&E), periodic acid schiff (PAS), resorcin fuchsin, sirius red and Gomori
- Immunohistochemical staining
- In situ hybridization
Nucleic acids purified from PF and PFPE tissue samples can be used for demanding downstream applications (see References, Technical Notes), including:
- RNA and miRNA profiling
- Long-range and multiplex PCR
- Next-generation sequencing
Proteins purified from PF and PFPE tissue samples can be used in a range of downstream applications (see References, Technical Notes), including:
- Western blotting
- Reverse-phase protein microarrays
- MALDI imaging mass spectrometry
- 2-D gel electrophoresis
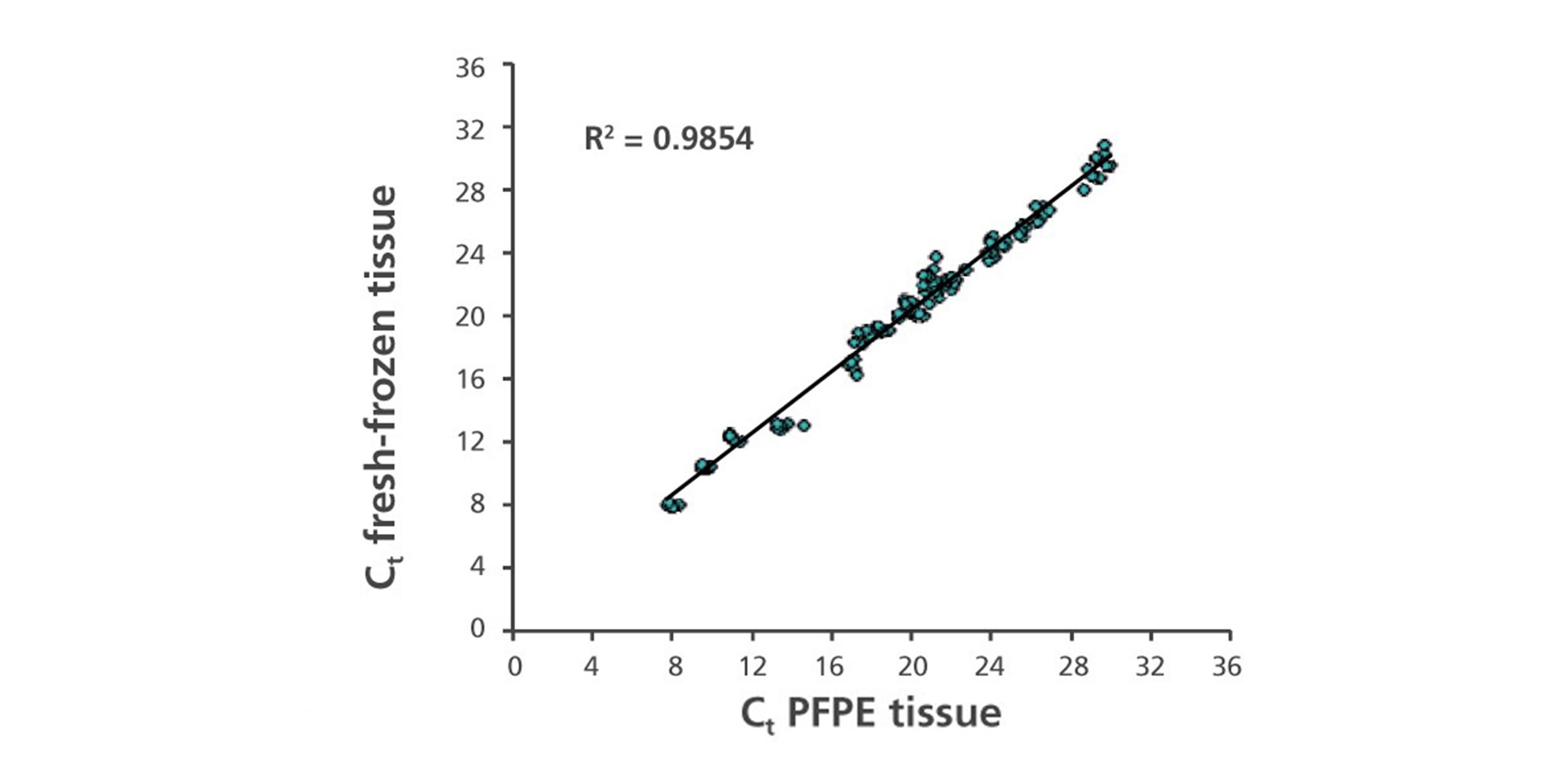
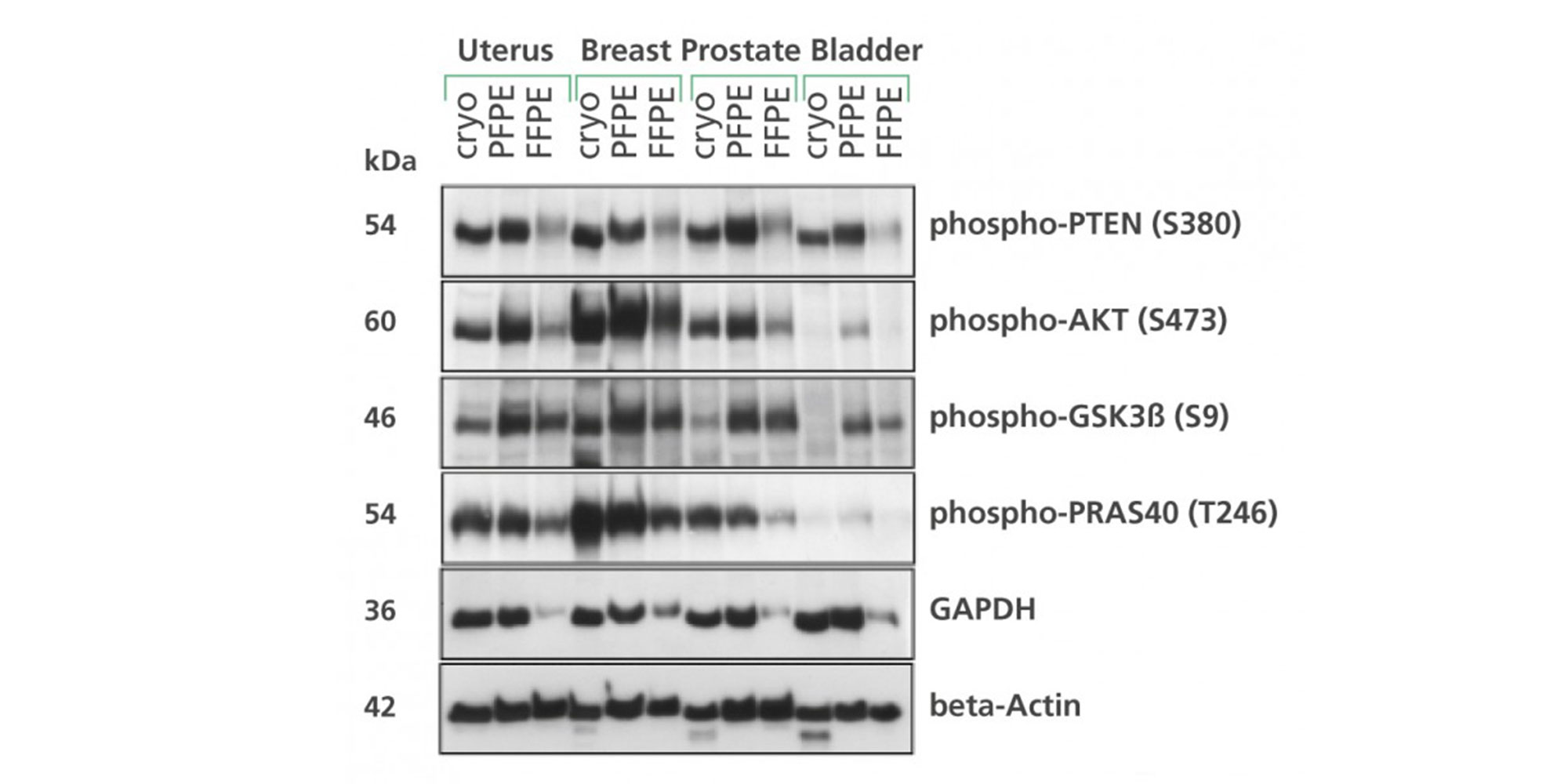
![Figure 7. RNA purified without chemical modification from PFPE tissue using the PAXgene Tissue RNA/miRNA Kit SYBR Green real-time RT-qPCR was performed with 10 ng RNA from cryopreserved, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) or PAXgene Tissue-fixed, paraffin-embedded (PFPE) rat tissue (modified according to Groelz et al. 2013). Depicted are the average delta-Ct values (delta-Ct = Ct[FFPE] – Ct[cryo] or delta-Ct = Ct[PFPE] – Ct[cryo]) from 6 different assays with amplicons ranging from 109 to 465 bp.](/storage/images/Content/Product_pages/Tissue/Fixation_Stabilization/SYBR_Green_real-tome_RT-qPCR_FFPE_PFPE.jpg)