Performance
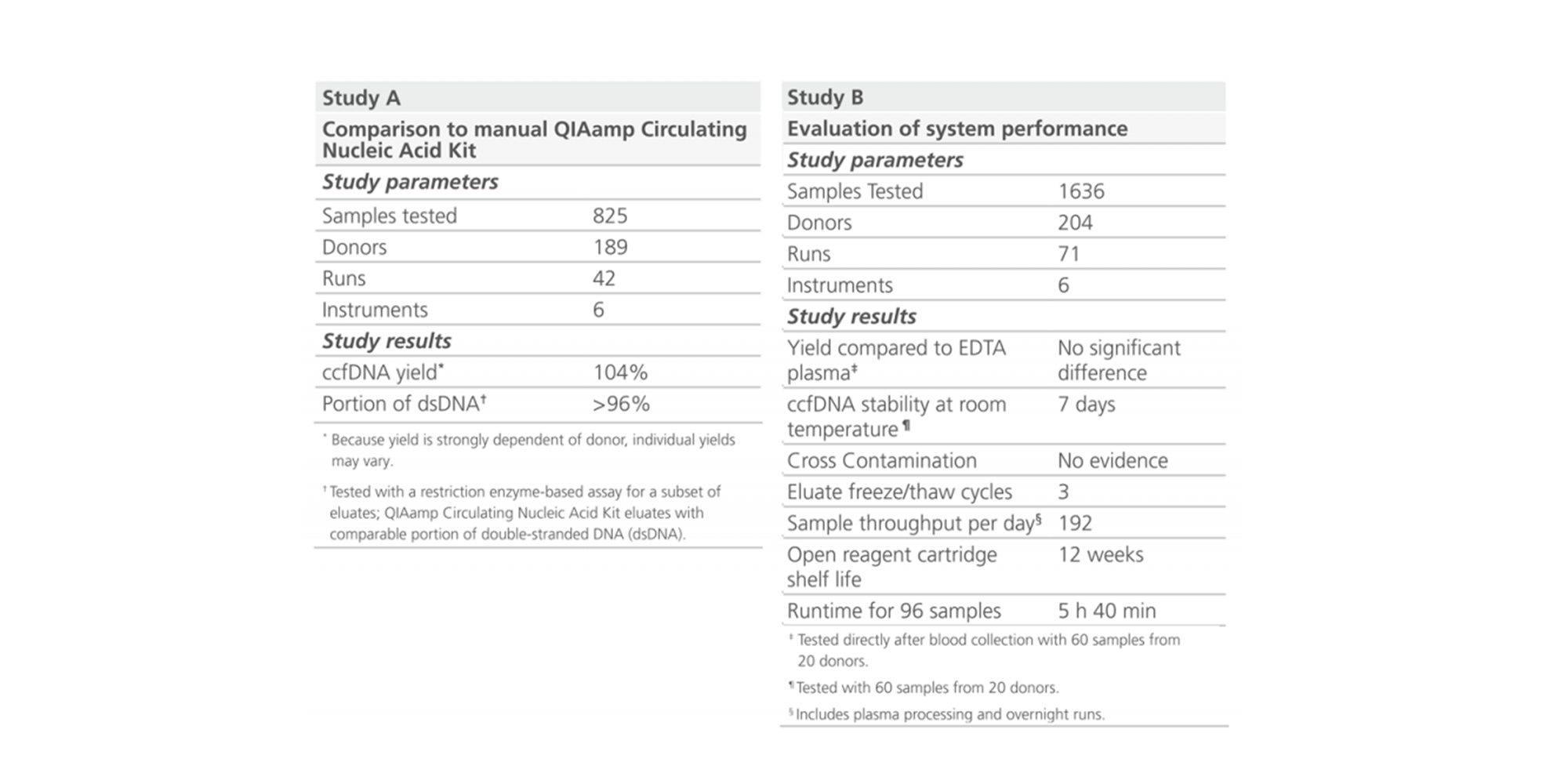
The fully automated QIAsymphony PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Kit procedure generates ccfDNA yields comparable to the manual QIAGEN QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit procedure (Figure 1). Since ccfDNA yield is strongly dependent of donor, individual yields may vary. Onboard measures of the QIAsymphony SP minimize cross-contamination.
Principle
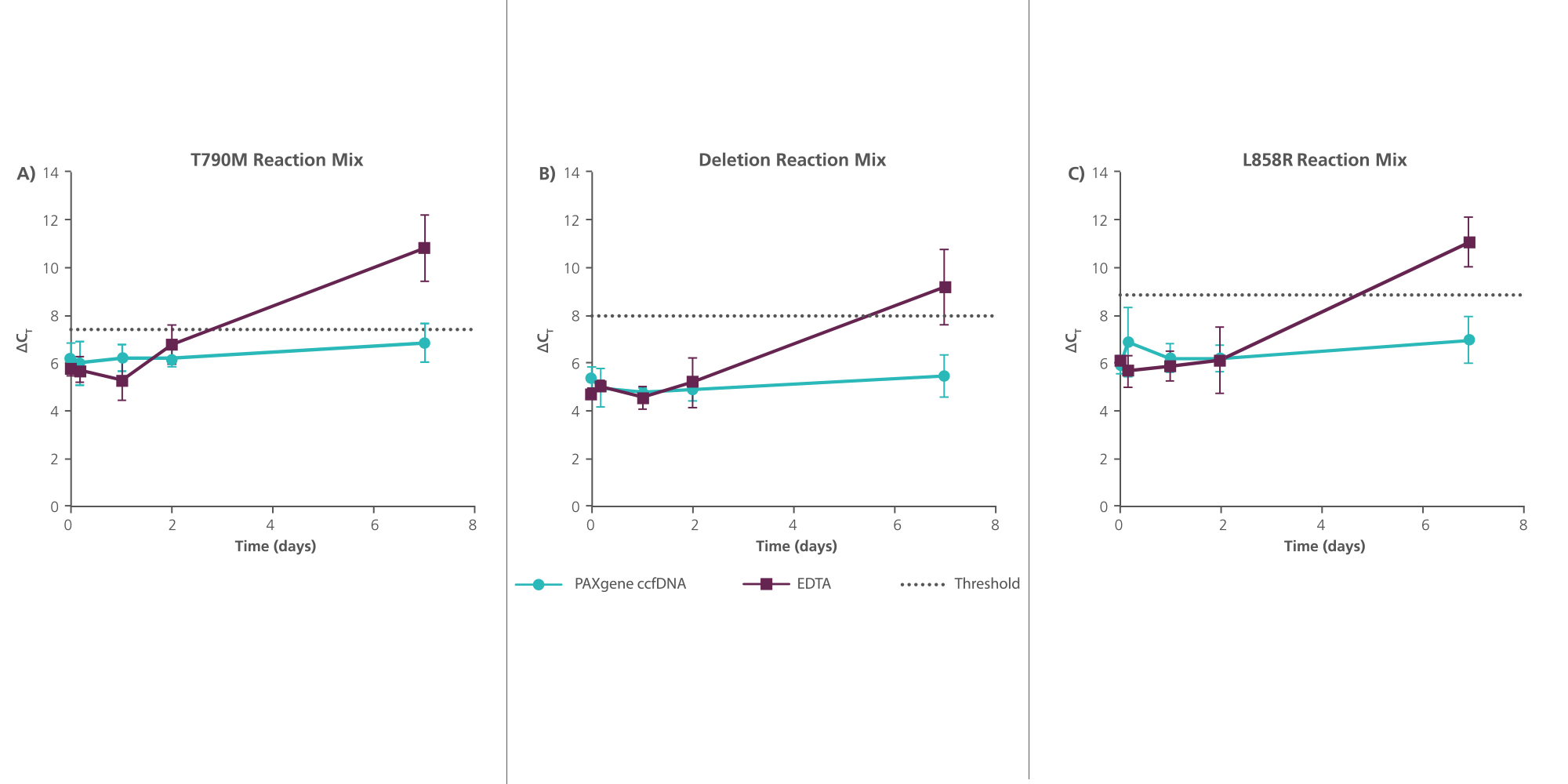
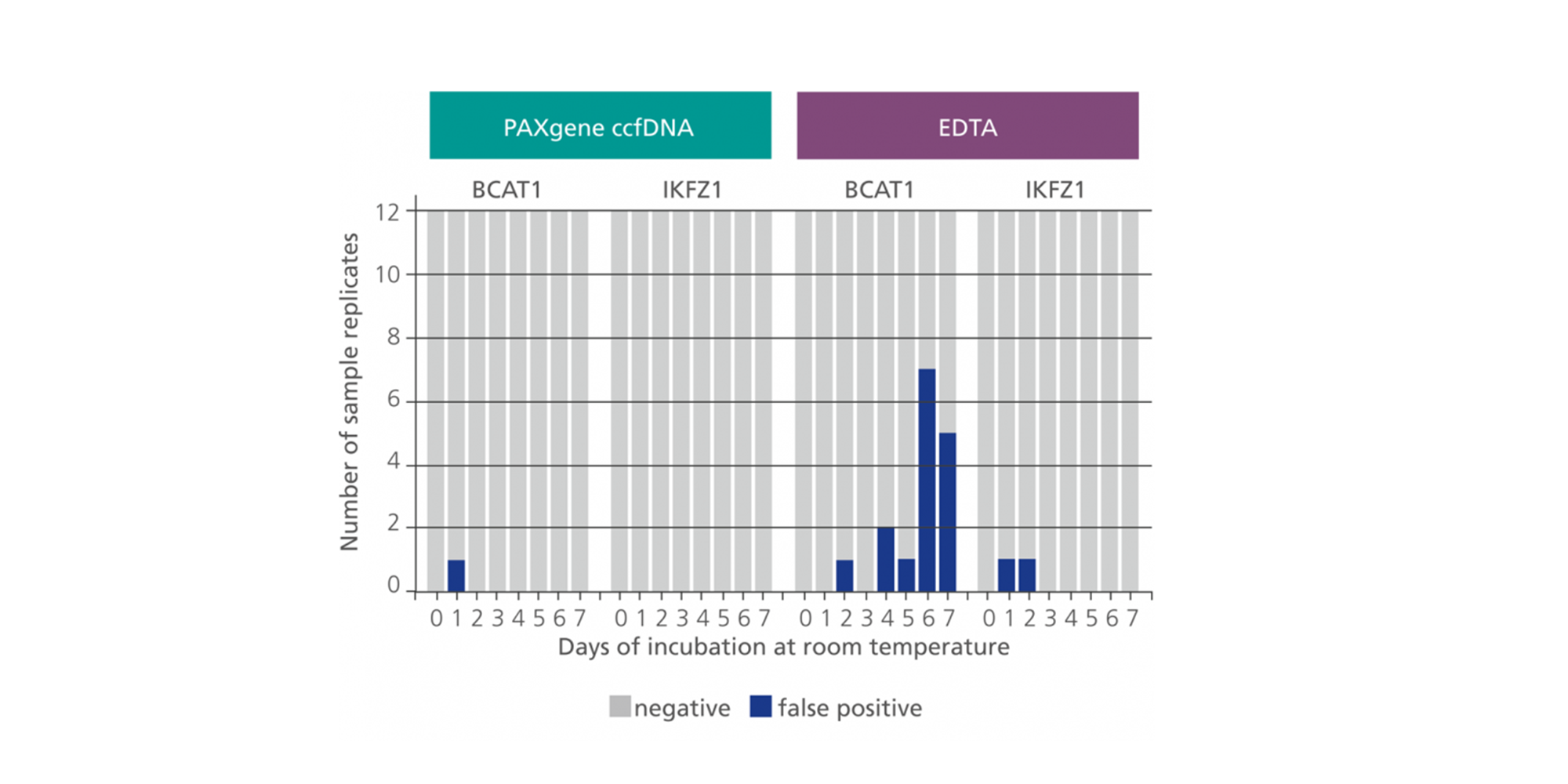
Apoptosis and lysis of white blood cells in unstabilized whole blood releases intracellular DNA into plasma, which dilutes naturally occurring ccfDNA. PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes contain an additive that anticoagulates blood and stabilizes blood cells via a non-crosslinking stabilization solution. This helps prevent the release of intracellular DNA and maintains constant ccfDNA levels during sample transport and storage prior to processing (Figure 2). When used with PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes, the proven magnetic particle technology of the QIAsymphony PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Kit provides a rapid, automated procedure to isolate ccfDNA of high quality and purity (Figure 3).
Procedure
The workflow begins with a centrifugation step that separates plasma from the cellular fraction of the whole blood collected into PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes. The plasma is then carefully transferred into a second tube. A second centrifugation step can be carried out optionally to further ensure separation of plasma from cellular debris. The purified plasma is then transferred to a third tube which is then loaded into the QIAsymphony SP.
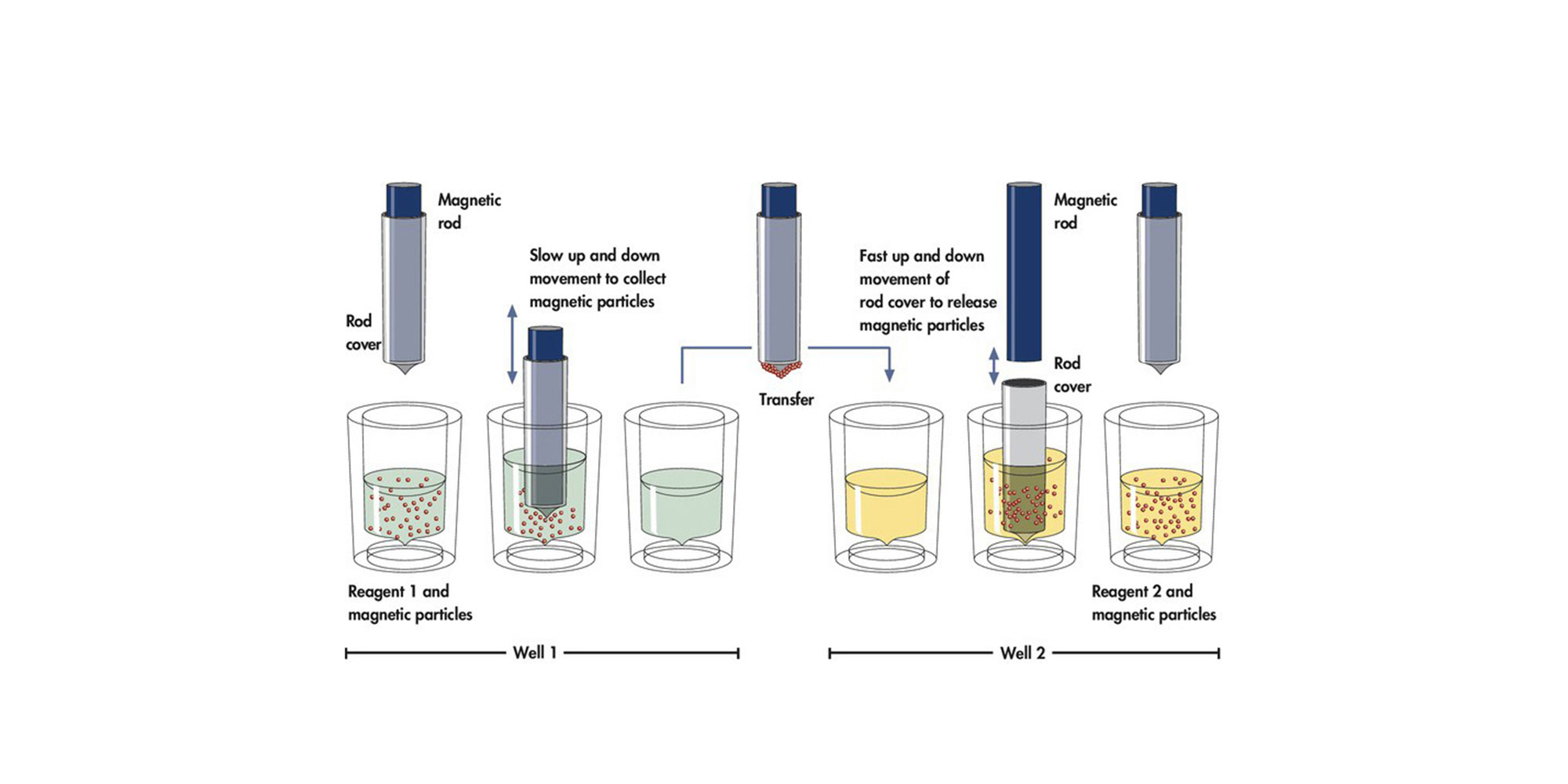
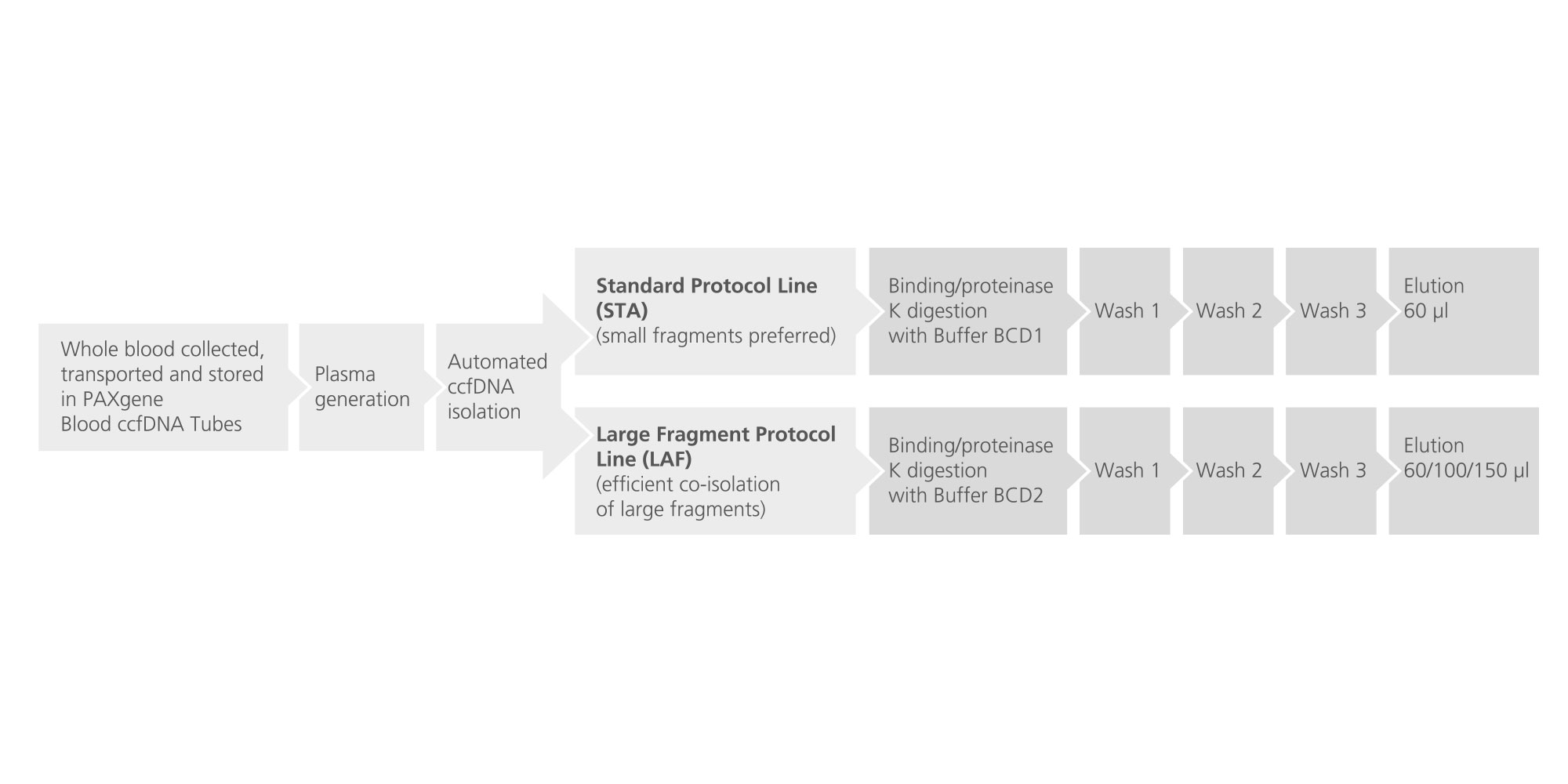
In the QIAsymphony SP, plasma proteins are digested by proteinase K while ccfDNA binds to the surface of magnetic beads (Figure 4). Depending on the chosen protocol line, predominantly small ccfDNA fragments or small and large ccfDNA fragments are isolated (Figure 5). Three wash steps ensure contaminant removal. Finally, ccfDNA is eluted from the magnetic particles and is ready for use in downstream applications.
Applications
ccfDNA purified using the QIAsymphony PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Kit and the QIAsymphony SP is ready for use in a wide range of downstream applications, including:
- PCR, including digital, multiplex and quantitative real-time PCR
- Pharmacogenomic studies
- SNP genotyping
- Next-generation sequencing
- Methylation assays